Pale toadstool dose. If life is dear to you: pale grebe poisoning
Everyone who likes to cook dishes from freshly picked mushrooms needs to know their main types. Otherwise, it is possible to get poisoned by eating poisonous instead of the usual mushroom. Of particular danger is pale toadstool, poisoning it can lead to death, which must be learned to distinguish from edible mushrooms.
The difference between pale toadstool and other mushrooms
Pictured is a pale toadstool
This is a very dangerous mushroom, since in most cases a person dies, poisoned by a grebe. Therefore, acquaintance with its appearance is one of the most important rules that a person must fulfill before going to the forest.
A pale toadstool usually has:
- The hat is egg-shaped or flat and convex, with a dry or mucous surface, diameter up to 12 cm, color from green to yellow or from off-white to brown, with dark fibers ingrown into it;
- White growths in the form of warts on a hat; older mushrooms may not have them, and they may disappear after rain;
- Hat plates are white, thin;
- The pulp is white;
- Leg up to 15 cm in length and up to 2 in width, thin, expanding to the base, white, white-green or white-yellow;
- Volvo - the formation at the lower base of the leg in the form of a cup, white, loosely contacts the leg, and moves away a few centimeters;
- The ring is a formation at the upper base, also white.
Toadstool can be confused with edible mushrooms, but such confusion can cost lives. To have a more complete picture, you need to know what damage this poisonous mushroom can do to the human body.
The action of poison toadstool on the human body

Pale grebe has a deadly toxin
Pale grebe is so poisonous due to the dangerous substances contained in it: phallus and amatoxins. The first ones are less toxic, but they spread faster through the blood, and you cannot get rid of them during heat treatment. The second is more poisonous, but not so fast. They are not digested in the stomach, but enter the liver, which is first destroyed.
Getting first into the stomach, and then into the blood, toxins do not manifest themselves in any way for several days. Even the destructive effect on internal organs is initially invisible, this is called the latent period. During this period, a person does not have symptoms of poisoning, but toxins trigger irreversible processes in the body, such as tissue necrosis.
Among these processes can be identified:
- Inflammation of the stomach;
- Destruction of the integrity of the liver and impaired functioning;
- Destruction of the structure of the intestines and other organs;
- Metabolic failure;
- Lowering blood glucose levels;
- Disruption of the central nervous system.
After several days of exposure to toxins on the body, helping a poisoned person is inconclusive. Therefore, even with the slightest doubt about your condition, you should contact the hospital. This must be done even if there are symptoms by which poisoning can be determined before the situation worsens.
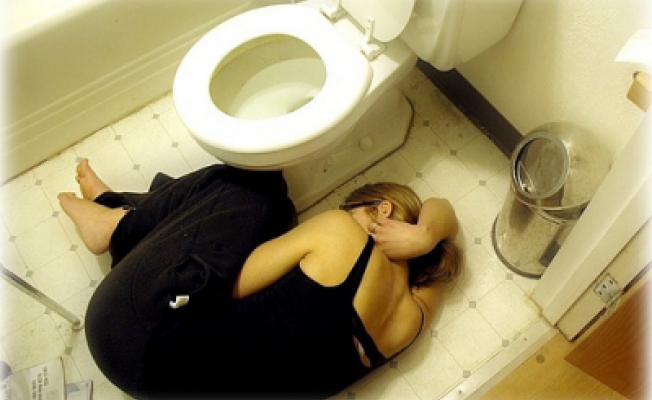

Vomiting, thirst, diarrhea, colic, abdominal cramps, dizziness can all indicate poisoning by a toadstool
Depending on the amount of poison received in the body, the person’s reaction to it and the period of poisoning, the symptoms are divided into several groups:
- Symptoms of the latent period. As mentioned above, during this period there are no signs of poisoning. Their absence can last from 7 hours to two days, usually about 12 hours. This time is an important criterion for diagnosis. But the longer it lasts, the more difficult the disease is. It is impossible to establish poisoning during this period, although poison already destroys the body;
- Pronounced symptoms. The duration of this period is from one to several days. Here the first symptoms begin to appear: incessant diarrhea with vomiting, thirst, colic and abdominal cramps. Thirst practically does not quench, all the drinkable liquid immediately comes out with vomiting. From dehydration, the pressure decreases, the face becomes pale, the lips turn blue, the color of the nails changes, the heartbeat becomes more frequent. Headache, dizziness, visual impairment may be present. Muscles cramps, arms and legs become cold;
- Imaginary recovery. This period lasts up to a day. It seems to the poisoned person that he is recovering, the symptoms of the second period disappear. Analyzes made at this time show the opposite. If the disease is severe, then on the third day death is possible. This period is crucial;
- The destruction of the body. If after three days of illness no help was provided, a person's eyes, mouth, and other mucous membranes turn yellow. You feel pain, heaviness under the ribs on the right side. Symptoms of the second period come back: diarrhea, abdominal pain. The kidneys stop working, toxic hepatitis develops. From kidney failure, destruction of the liver and disturbances in the functioning of the heart, death can occur. This occurs in severe cases and untimely visits to the doctor.
Death occurs with severe poisoning. If you ask for help in time, this will not happen.
First aid for poisonous grebe poisoning

In case of pale toad poisoning, call an ambulance
First aid will not have a noticeable effect, but can alleviate symptoms. Before that, you must definitely call a doctor and provide first aid while the ambulance is traveling. If you suspect poisoning with a grebe, they primarily cause vomiting, cleansing the stomach, and neutralize the effect of toxins:
- Take half a liter or a liter of clean water, drink it, followed by vomiting. The procedure is repeated several times;
- Activated carbon or other sorbents are taken according to the instructions.
These actions are not a cure, and doing them yourself is useless. First aid will only help to correctly use the time before the doctor arrives. Anyone who could be poisoned even without the presence of the disease should contact the hospital.
The treatment itself is difficult and includes a complex for the removal of poison. Different drugs are used, but one that can cure this particular disease has not yet been invented.
Poisoning treatment
There is no universal cure for pale grebe poisoning. The action of the poison can be removed by some antibiotics. The treatment is aimed at reducing the intensity of symptoms and neutralizing toxins:
- The stomach is washed regardless of whether it was done during first aid. The fungus might not completely exit the stomach, as it is not digested;
- If the poisoning occurred no more than three days ago, benzyl penicillin is used 6 times a day with a dosage of 500 thousand - 1 million per kilogram of weight. Up to 12 days, silibinin is used at a dosage of 30 mg per kilogram of body weight per day. Perhaps the use of lipoic (thioctic) acid;
- Crystalloid solutions are administered intravenously to prevent dehydration. Due to a decrease in glucose, it is also injected into the body. The patient is watered with salt water to replenish the chlorides;
- For the removal of toxins, forced diuresis and extracorporeal detoxification are used. Their essence is to stimulate the work of the necessary organs in order to eliminate toxins;
- They give drugs that support the cardiovascular system, bringing it into tone;
- Enzymes are used to lower blood coagulation;
- To restore the functioning of the liver and kidneys, vitamins are given to the patient.
In case of pale toadstool poisoning, treatment is reduced to toxin neutralization and is carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor
These are the main treatments. The rest depend on the severity of the disease, the patient's condition. Each case is individual, but when you go to the hospital within 36 hours after poisoning, the chances of recovery increase.
Although it is possible to recover, it is never easy. After taking the right drugs and getting medical help, it is important to follow some measures so as not to aggravate the situation.
Pale Toad Poisoning Prevention
Following the rules after treatment will help to avoid the serious consequences of poisoning. This can be both the failure of some organs, and the development of other diseases, which is why a second visit to the hospital is possible.
It is necessary to comply with all the doctor's prescriptions. This can usually be diet and prescription medication. Also, after leaving the hospital, it is advisable to be observed in the hospital for some time to eliminate the troubles described above.
To be sure that the mushroom collected in the forest is not a pale grebe, it is better:
- Do not collect suspicious, toadstool, strange looking mushrooms;
- To get acquainted with the main types of edible mushrooms and be guided by this knowledge when collecting;
- Do not collect mushrooms having a Volvo and a ring at the same time or one thing if there is no confidence in its edibility;
- Remember that toxins are not killed by heat treatment.
And do not forget that white grebe is one of the most poisonous mushrooms in the world. Knowing about its effect on the human body and how it looks, avoiding such mushrooms is the best prevention from poisoning.
Watch a video about pale grebe and how to distinguish it from other edible mushrooms.
Mushrooms are a tasty and healthy product that both adults and children cannot resist. But you need to be very careful when collecting and cooking mushrooms, because it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between an edible species and an inedible one, which can lead to serious consequences and even death. Analysis of statistics showed that amateur mushroom pickers most often suffer from poisonous grebe poisoning - people who decided to go into the forest for their own pleasure, not even knowing the basic rules.
In order to protect yourself from poisoning and the consequences that follow it, you need to understand the distinguishing features of a pale toadstool:
- The body is represented by a shape that looks like an egg.
- The mushroom is almost completely covered with a transparent film. You can feel it if you hold your palm over the mushroom.
- The hat is greenish or light gray in color does not exceed 15 cm, and the shape differs depending on the location and age of the fungus and can be represented as a flat or hemispherical shape.
- The fleshy flesh is white in color, which does not change even when damage occurs.
- Volvo, which reaches about 4-5 cm in width. This feature can be considered one of the most important, since it almost never occurs in edible mushrooms.
Despite the fact that the pale grebe has distinctive features that would seem to help mushroom lovers when collecting, errors still occur. Confusion occurs for two reasons, namely:
- Inattention and simple self-confidence. Many people think that they can easily detect a poisonous mushroom, and therefore do not pay attention to such recommendations.
- An accident that can be explained by the similarities between different mushrooms.
At the same time, the usual academic awareness may save the situation and protect consumers from severe poisoning. So, we suggest using an example to consider similar mushrooms and identify features that will allow differentiation: 
- although greenfinch and russula are similar in color, they do not have volva rings. Therefore, as if I would not like to quickly cope with the task and collect the mushrooms, we advise you to look at the base and leg, below which is the same Volvo.
- in champignons, age-related changes occur, which lead to the fact that the hat plates become brown.
- floats that are not only ringless but also too small to be confused.
REMEMBER! In order not to make a mistake, do not cut off the mushroom caps, because this will not allow you to see a Volvo and a ring of pale toadstool - mortally dangerous for humans due to the presence of a toxin such as amanitotoxin.
What happens if you eat a pale toadstool?
Toadstool is a deadly mushroom, and therefore its use in food is strictly prohibited. As a result, severe poisoning appears, which will be accompanied by severe pain, colic and cramps, causing death.
The consequence of pale grebe poisoning is a rapidly developing and progressive phalloidin syndrome, which manifests itself in the gradual destruction of organs such as the kidneys, liver and gastrointestinal tract. In addition, under the influence of toxins, which are found in large quantities in the fungus, necrosis soon develops.
Elder people and children who have weakened immunity most often die from such poisoning, which makes him incapable of even resisting toxic toxins for the first time. It is known that even a piece of pale toadstool may be enough for a fatal outcome, not to mention a whole mushroom. Do not be mistaken on the account that with high-quality heat treatment all harmful properties disappear and the mushroom becomes safe for humans, as this is not true.
IT'S IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Not only the body of the fungus is poisonous, but the spores that are carried with the wind are very dangerous for humans. After all, if spores are caught, even an edible tasty mushroom can turn into a deadly weapon! Therefore, you should not pick mushrooms where you saw a pale grebe.
Amanitotoxin or why is the poison of the toadstool deadly?
In a pale grebe two completely different groups of toxins are presented, which differ in the strength and speed of exposure to the human body:
- alpha amanites (amanitotoxins);
- phalloidins.
Amanitotoxins are toxins that, although they act more slowly than phalloidins, are more dangerous. This is because their lethal dose is several times less than any other poison. They do not weaken and do not collapse upon drying or heat treatment, they are not digested and certainly not absorbed. After the toxins pass through the intestines, they end up in one of the most vulnerable places - the liver - the organ to which all the power of the killing poison is directed.
In addition, toxins cause negative effects such as:
- the gradual destruction of cells, which causes degeneration of the liver;
- drop in glucose to a critical point;
- destruction of the nervous system, which is clearly manifested in the last stages of poisoning with white grebe.
What are the symptoms of pale grebe poisoning?
Poisoning occurs unevenly, has several stages, which are accompanied by certain symptoms. Symptoms may differ depending on the amount of grebes eaten, that is, on the “portion” of poison ingested by the body, as well as on the condition of the person himself (general health, age, gender, and even the presence of chronic diseases). 
There are several stages that have their own specific characteristics:
- The first (latent) period during which a person feels excellent and does not feel even the slightest discomfort. This condition lasts up to 40 hours. If you manage to somehow discover that the food you eat was poisonous, then the chance of saving a person increases. But this happens extremely rarely, which negatively affects the subsequent state, because toxins penetrate the blood at a tremendous speed and begin to confidently move to the ultimate goal - the destruction of the body.
- The second period does not appear immediately, which can lead a person astray and make you think about ordinary food poisoning. Symptoms begin to appear after a day, but sometimes the appearance of signs of poisoning occurs already after 5-6 days.
At this time, the condition worsens with every minute, and poor health manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- severe diarrhea, in which diarrhea is not only a strange yellowish color, but also has a watery structure. After a while, small blood clots may appear;
- vomiting and imbalance in the body. If you try to drink at least a couple of sips of water, vomiting resumes with greater force;
- the appearance of cramps and terrible pain in the intestines and abdomen;
- dizziness, weakness, and severe headache (sometimes, knocking at the temples);
- increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure;
- deterioration of visual reflexes, which leads to the fact that the picture in front of the eyes is very blurry;
- cramps that cause severe pain in the legs;
- minimal or no urination.
- The third period, during which there is a significant improvement in the condition, unfortunately, is imaginary. Despite the fact that the symptoms disappear, the body continues to break down, which is especially evident in such an analysis as blood biochemistry. Doctors even consider this ten-hour period the most dangerous, because often there is drowsiness, against which death occurs as a result of collapse.
- The fourth period in which all organs are affected. At the last stage, all signs of poisoning are renewed with renewed vigor. In addition, the eyes and oral cavity acquire an unpleasant yellow color, as well as pain in the hypochondrium, especially right. In severe poisoning, failure quickly develops: hepatic and renal, which lead to quick and painful death.
Of course, death does not occur in all cases. A favorable outcome can be affected by several reasons, among which the victim’s good health (strong heart, excellent state of blood vessels and nervous system), as well as a mild poisoning, in which recovery takes only a few days. With serious intoxication, it may take more than one week or even a month, but when all medical recommendations are followed, the organs will completely recover, and the yellow color will disappear in the first few weeks.
The first "home" help in detecting signs of poisoning
Despite the fact that, in this case, it will be practically useless and will not bring absolutely any positive effect. If you think that the poisoning was triggered by a pale toadstool, you should immediately call a doctor or go to the hospital yourself, in which all the necessary tests will be performed. Turning to a specialist during the first 36 hours is a great chance for a full recovery. By the way, even if signs of poisoning appeared in one person, then you need to start treatment for everyone who could also taste poisonous mushrooms, because slowing down can lead to death.
Therefore, first aid is relevant only until the arrival of an ambulance. For starters, it is recommended to rinse the stomach, cleansing it of everything, including pale toadstools. It will be enough to drink up to 2 liters of water, depending on the mass, and “tear” all the contents. The adoption of activated carbon in the usual proportion will not be superfluous.
REMEMBER! Self-medication must be minimized, because it can harm the patient.
Features of treatment for pale grebe poisoning
It is not easy to deal with such poisoning, since it not only affects the digestive tract, but penetrates the blood almost instantly. The actions that are carried out in the hospital are quite simple, but this does not mean that they should be repeated at home: 
- gastric lavage, which is not dependent on the presence of vomiting, as particles of pale grebe can still be inside;
- the use of antidotes. Since there is no special antidote, drugs such as benzene-penicillin, silibinin, and sometimes citric acid, are used. At the same time, the quantity and order of application that doctors are counting on the basis of the stage of poisoning, health and human condition is important;
- elimination of an important problem - dehydration, which is provoked by vomiting. A patient is given a dropper, and various devices are administered intravenously. If necessary, the victim is given salt water, which should replenish the amount of chloride in the body;
- conducting forced diuresis and hemosorption, which help with the removal of harmful substances;
- prescribing cardiac drugs that the heart needs to restore proper functioning;
- the use of proteolytic substances that are aimed at preventing disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- special therapy (liver), which is carried out with the help of replenishing vitamins belonging to group B.
The main thing to remember is that treatment is more effective when treated in the early stages. Poisoning with a pale toadstool is very dangerous and can lead to serious consequences, including death. Therefore, we again warn that it is not necessary to carry out the treatment yourself, because for this there are specialists who know what needs to be done and what actions to take.
How to protect yourself from mushroom poisoning?
Caution is the first and most important rule to remember when you are going to the forest for mushrooms. Always remember that if there is at least some doubt that the mushroom is edible, you should not try your luck and try it, as this can negatively affect your health and result in severe poisoning.
We offer several rules that will help you save your own life:
- often poisoning occurs when by chance a person mixes or confuses a pale toadstool with an edible mushroom (for example,);
- a distinctive feature of the disease is the manifestation of symptoms in the form of vomiting and diarrhea after a long period;
- when poisoning one of the group members, you should also seek help and pass all the necessary tests.
Not a single mushroom does such a destructive harm to the human body as white grebe. This is the most dangerous and poisonous mushroom. Eating it for food becomes a cause of severe poisoning, treatment of which must be started as quickly as possible. But this dangerous mushroom itself, or rather its individual components, can help in the treatment of cancer.
Appearance
Pale grebe can be found in coniferous and deciduous forests. It grows in groups, occasionally singly throughout the summer and before the onset of frost.
Pale grebe is very poisonous. The fungus contains deadly poisons: phallotoxins and aminotoxins. All parts of the fungus are poisonous, including spores. Even the juice remaining on the knife after the cut of the mushroom is enough for a person to be poisoned.
Pale toadstool has white flesh and pleasant mushroom aroma. Inexperienced mushroom pickers often confuse pale toadstool with ordinary edible champignons, russula, honey agarics. In contrast, the pale grebe on the lower part of the leg has a tuberous swelling, and at the top there is a ring in the form of a white “skirt”.
The venom of a pale toadstool cannot be neutralized by heat treatment.
Photo of a pale toadstool
The effect of poison on the human body
When even a small particle of the fungus enters the gastrointestinal tract, intoxication of the body occurs. Mostly the liver and kidneys suffer, where the concentration of poison occurs.
Under the influence of poisons, liver cells die and liver failure develops, and kidneys degenerate. Gradually, all human organs are affected. If you miss the time and do not take urgent measures, treatment may be useless. All drugs will be powerless against intoxication.
The most difficult to tolerate poisoning is children and the elderly, among them the largest number of fatal cases.
Timely seeking medical help with the slightest suspicion of poisoning with a pale grebe will reduce the likelihood of death by 50%.

If even a small piece of mushroom enters the body, poisoning occurs.
Symptoms of Poisoning
The first signs of poisoning may appear after 12-13 hours.
Typical symptoms:
- spasmodic abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- rampant vomiting;
- frequent loose stools with an admixture of blood in the feces;
- pale face, wet palms;
- visual impairment;
- prostration.
Help with poisoning
At the slightest sign of poisoning, you should immediately call an ambulance or in any other way deliver the victim to the hospital. Otherwise, the treatment may be unsuccessful.
Before the ambulance arrives you should:
- Rinse the stomach, drink 5-6 glasses of warm boiled water.
- Induce vomiting. Repeat the procedure several times.
- Drink a laxative. Castor oil can be used as a laxative.
- Make an enema. All this is done in order to cleanse the stomach and intestines from food containing poison.
- Lie in bed and attach warm warmers to your limbs.
- Do not eat or drink alcohol.
The life of a person depends on how quickly treatment is started.

At the slightest sign of mushroom poisoning, an ambulance must be urgently called
Resuscitation
There is only one prescription for treating a patient with pale toadstool poisoning - eliminating dehydration, detoxifying and preventing death. Treatment begins with the use of various plasma substitutes, which are administered in a volume of at least 3-5 liters per day with a dropper. In case of poisoning, a drop in blood pressure is observed, measures are taken to increase it. For this, norepinephrine or mesatone is administered. Hydrocortisone or other medicinal analogues are used to support the liver. If there are signs of heart failure, strophanthin, korglikon are used.
(No ratings yet)
Pale toadstool is considered the most poisonous mushroom in our area. Moreover, all its parts are dangerous. These mushrooms are categorically not recommended to be picked, since even at the slightest contact with the edible type, the poison of the toadstool is quickly absorbed into the caps and legs of a good mushroom. Outwardly, the grebe does not cause any suspicion, it has a pleasant smell and taste. Often, poisonous toadstools are brought instead of honey mushrooms, or confused with other species. Therefore, you need to know the distinctive features that avoid poisoning and more serious consequences.
Distinctive features of the grebe pale
Pale toadstool has a bonnet. The hat has a yellowish color, varies in size from 4 to 12 cm. At a young age, there are white warts on its surface, which are absent in adult fruits. The leg has a cylindrical shape, 10-15 cm in size. In the upper part of the leg there is an upright white ring.
Young fruits of the toadstool can be confused with russula, champignons, rows, often poisonous toadstools are brought instead of mushrooms.
You can distinguish this mushroom from russula by such signs:
- Russula lacks tuberoid thickening and Volvo;
- The Russula has a straight and straight leg without a ring.
The difference between pale toadstool and champignon is not always immediately apparent. Their legs are exactly the same. You can determine by the plates on the inside of the cap. It is always white in a toadstool; champignon has pinkish or brown plates with age. The young fruits, given the description of the pale grebe, are very difficult to distinguish; only an experienced mushroom picker can do this, relying on their intuition. If there is even the slightest doubt, it is not recommended to collect such mushrooms.
Properties and poisonous toadstool
Pale toadstool contains very strong toxins, which, when ingested with a concentration of 1 gram per 1 kg of body weight, lead to death. When a small part of the poisonous pulp gets into the dish, it makes the entire batch toxic. The fungus contains 2 types of alkaloids:
- Amanitin - a very strong slow-acting poison
- Phalloidin is a fast-acting substance, no less toxic.
These poisons are damaging to the kidneys and liver of a person, killing him in just a few days. The danger is that the first signs of poisoning can occur even on the second day, and during this time necrosis of all tissues develops from the action of toxins. After several days of such an action, treatment often does not bring any results.
In addition, the mushroom has some positive properties:
- Igo can be used for homeopathic purposes as an antidote to some types of poisonous mushrooms.
- Injections with minimal doses of toxins toxins are administered to heal and rejuvenate the skin.
- In folk medicine, they make tinctures from a pale toadstool for the treatment of cancer.
- Some use the mushroom as a means of combating harmful insects.
However, the use of pale toadstool is minimal, in comparison with its danger, therefore, any contact with it should be avoided.
Symptoms of Poisoning
The symptoms that appear will depend on the amount of fungus eaten. Such stages of poisoning are distinguished, for which their signs will be characteristic:
- Latent phase. Symptoms are absent during this period. Typically, exposure to toxins occurs within 12 hours before the first unpleasant signs appear, although it can last up to 2 days. It is almost impossible to establish poisoning at this stage, the longer it lasts, the less likely it is to save a person.
- Acute period. It begins after the onset of symptoms of intoxication and lasts 1-2 days. A person is tormented by severe pain in the abdomen and head, diarrhea, vomiting, unquenchable thirst, dizziness. The skin turns blue, the heartbeat is quickening, the limbs are cold, prone to seizures. Signs of dehydration are also pronounced.
- Stage of relief. It is characterized by the fact that a person feels better, acute symptoms subside, the patient believes that he is recovering. The severity of the situation can be determined by analysis, if they are far from the norm, then on the third day a fatal outcome is possible.
- Complete destruction of the body. If after 3 days a person has not received the necessary medical care, then all internal organs are destroyed. Vivid symptoms resume with greater intensity, mucous membranes begin to turn yellow. Death can occur due to renal failure, impaired liver and heart function.
Such an outcome only happens when poisoning of toadstools in large quantities has occurred, or timely assistance has not been provided to the victim. In the best case, a person is almost always saved.
First aid
At the first symptoms of poisoning, first of all, a team of medical workers is called. Prior to their arrival, first aid should be provided to the injured person in order to reduce the risk of irreversible consequences for human health and life.
 First of all, a person needs to do a gastric lavage. To do this, you can use a weak solution of potassium permanganate, or plain warm water, dissolving the salt in it: 1 tablespoon per glass of water. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid at a time. Then induce vomiting by pressing fingers on the root of the tongue.
First of all, a person needs to do a gastric lavage. To do this, you can use a weak solution of potassium permanganate, or plain warm water, dissolving the salt in it: 1 tablespoon per glass of water. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid at a time. Then induce vomiting by pressing fingers on the root of the tongue.
After washing the stomach of the victim, it is necessary to lay and put a warm heating pad on the lower extremities and stomach. Give a sorbent to drink, you can activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight.
Further treatment is carried out by medical specialists, after finding out which mushroom provoked intoxication (if the patient has vomit, they can be used for laboratory studies of the nature of toxins).
First of all, treatment will be aimed at eliminating dehydration and removing intoxication; for this, saline and glucose with insulin are dripped. Next, some antibacterial drugs that have antidote properties are prescribed. They also carry out therapy to support the work of the heart, kidneys and liver.
The treatment takes a very long time, up to 4 weeks. If therapy gives positive results, then the prognosis is favorable and soon recovery will begin and complete restoration of the functions of all internal organs and systems.
White grebe is a very dangerous mushroom, which has minimal differences with edible species. Therefore, if there is no good knowledge in the mushroom field, it is better not to do this business on your own, but to trust specialists.
Going on an autumn day to the forest for mushrooms, you need to remember that not every mushroom that attracts external attractiveness is safe for health. Among the vast kingdom of mushrooms, pale grebe is especially insidious. It has a pleasant mushroom aroma and taste that can win the heart of the gourmet. But at the same time it is the most insidious and dangerous among poisonous mushrooms.
The ancient Roman emperor Claudius, seduced by the exquisite taste of mushrooms, could not restrain his enthusiasm and ordered henceforth to always serve him such mushrooms. However, the desire was not destined to come true, poisoning with a pale grebe happened very quickly. The next day, Claudius died of a lethal dose.
The hallmarks of the fungus
Inexperienced mushroom pickers often become victims of the poisonous grebe. Often mistaken for green russula, champignon, greenfinch. However, the grebe has significant differences that you need to know about. Toadstool mushroom at a young age has an ovoid body, completely covered with a film. The hat is 5-15 cm light olive or grayish in color with a hemispherical or flat shape. The flesh of a pale toadstool is fleshy, white, does not change color when damaged. A distinctive feature of the fungus is the presence of a well-defined Volvo about 5 cm wide, which is practically absent in edible mushrooms.
Irreversible consequences
Pale grebe poisoning occurs after eating it. The fungus is poisonous not only the body, but also its spores. They have the ability to spread with the help of wind and settle on plants within a radius of three meters. Therefore, it is impossible to collect edible mushrooms that grow in the immediate vicinity of the toadstool.
After the poisonous mushroom enters the body, the pale toadstool toxin does not act immediately, initially showing no signs of poisoning. Some time after eating a pale toadstool, the first signs of poisoning appear. Symptoms of poisoning appear only after 8–36 hours, and at this time the body is already receiving irreparable harm.
To get a lethal dose of poison, just eat 30 grams of fruiting body. Due to its pleasant taste, the grebe cannot be distinguished from edible mushrooms. Its poisons are not digested in the stomach and are not neutralized even after prolonged heat treatment at 100 degrees, drying or freezing.
The composition of this dangerous fungus includes a potent fungal toxin - amanitin. He and phalloidin are classified as polypeptides. They primarily affect the cells of the liver, kidneys, central nervous system, damage the spleen cells and heart muscle.
From a strong toxic effect on the main organs of a person, an antidote practically does not exist.
![]()
- At the first stage, there are no symptoms of poisoning, the victim feels fine and does not suspect anything bad.
- After 1-2 days, after damage to the mucous membrane of the small intestine, acute pain in the abdominal cavity, vomiting, diarrhea begin.
- Then comes the "period of imaginary well-being", there are signs of improvement in the patient's condition. The victim feels well and seems to be recovering, but the disease continues to progress.
- At the last stage of pale grebe poisoning, renal and hepatic insufficiency appear. At this point, the victim may die.
The following symptoms are characteristic of poisonous mushroom poisoning:
- vomiting
- intestinal colic
- stomach ache,
- thirst,
- diarrhea with blood
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes,
- possible cramps and lowering of temperature,
- muscle pain
- visual impairment
- the pulse is weakening.
The degree of poisoning:
- With mild poisoning, symptoms of moderate gastroenteritis and minor liver damage are noted.
- The average degree of poisoning is characterized by pronounced gastroenteritis, toxic damage to the liver and kidneys.
- Severe poisoning entails irreversible changes in the internal organs, liver and kidney failure. After the appearance of such symptoms, the likelihood of death increases, any treatment becomes useless.
In 90% of cases, poisoning with a toadstool is fatal.

When poisoning with a pale toadstool, vomiting and diarrhea are characteristic
The provision of first aid at home
Despite the disappointing predictions, in medical practice there are many cases when, after poisoning with a pale toadstool, treatment started with modern antidotes saved a person’s life on time.
If the first symptoms of poisoning appear and there is a suspicion that this was due to eating mushrooms, then it is urgent to give the victim first aid at home and immediately seek medical treatment.
Timely diagnosis in a hospital and immediately started treatment give a chance to save the victim.
First aid at home is required for symptoms of poisoning such as general weakness, persistent vomiting, diarrhea. First of all, the victim needs to rinse the stomach so that the mushroom toxin does not spread further throughout the body. For this, the patient needs to drink half a liter of boiled water, with the addition of a teaspoon of salt, soda or 2-3 crystals of potassium permanganate. Further help in cleansing the stomach is to induce vomiting in a person by pressing on the root of the tongue. As an antidote, with first aid give activated charcoal at the rate of: one tablet per 20 kg of weight.
The use of medicinal plants after the diagnosis of the first signs of poisoning will be of great help, having a positive effect on the course of further treatment. Studies by experts confirm that the herb thistle spotted helps very well as an antidote for poisoning with a pale toadstool. The unique plant is absolutely harmless and practically has no contraindications in use. Milk thistle is an excellent hepatoprotector, it prevents the absorption of toxic substances in the liver, will provide first aid as an antidote in the neutralization of toxic substances. To prepare the antidote, it is necessary to pour 1 teaspoon of the herb with a glass of boiling water, steam the composition in a water bath for 25 minutes, insist, strain and take 1/3 cup three times a day.
Remember that with poisonous grebe poisoning, every second counts! Therefore, try to self-medicate less.







